The 9 Things That Affect CPU Performance
Introduction
When it comes to the performance of a computer, the central processing unit (CPU) plays a vital role. The CPU is often referred to as the “brain” of the computer, as it carries out most of the processing tasks. However, not all CPUs are created equal, and various factors can impact their performance. In this article, we will explore the nine key things that affect CPU performance and understand how they can impact the overall speed and efficiency of a computer system.
1. Clock Speed
Clock speed, measured in gigahertz (GHz), refers to the number of cycles a CPU can execute per second. A higher clock speed generally results in faster processing, as it allows the CPU to perform more operations within a given time frame. However, it’s important to note that clock speed alone does not determine the overall performance, as other factors come into play.
2. Cache Size
The CPU cache is a small, high-speed memory that stores frequently accessed data for quick retrieval. A larger cache size enables the CPU to access frequently used instructions and data faster, reducing the time it takes to fetch information from the main memory. Thus, a CPU with a larger cache size tends to offer better performance in tasks that rely heavily on cache utilization, such as gaming or video editing.
3. Number of Cores
Modern CPUs often come with multiple cores, which are individual processing units within a single chip. The number of cores determines how many tasks the CPU can handle simultaneously. Having more cores allows for better multitasking and improved performance in applications that can utilize multiple cores effectively, such as video rendering or data analysis.
4. Instruction Set Architecture
The instruction set architecture (ISA) defines the set of instructions that a CPU can execute. Different ISAs have varying capabilities and efficiencies. For example, x86 and ARM are two popular ISAs used in desktop and mobile CPUs, respectively. Choosing the right ISA for a specific task can significantly impact the CPU’s performance and energy efficiency.
5. Thermal Design Power (TDP)
Thermal Design Power (TDP) is the maximum amount of heat that a CPU generates and needs to dissipate under normal operating conditions. CPUs with higher TDP ratings generally require more robust cooling solutions to maintain optimal performance. Overheating can lead to thermal throttling, where the CPU reduces its clock speed to prevent damage, resulting in decreased performance.
6. Overclocking
Overclocking is the process of increasing a CPU’s clock speed beyond its default specifications to achieve higher performance. However, this also leads to increased heat generation and power consumption. Overclocking can provide a significant boost in performance for tasks that heavily rely on CPU speed, such as gaming or 3D rendering. However, it should be done with caution, as it can also decrease the lifespan of the CPU and void warranties.
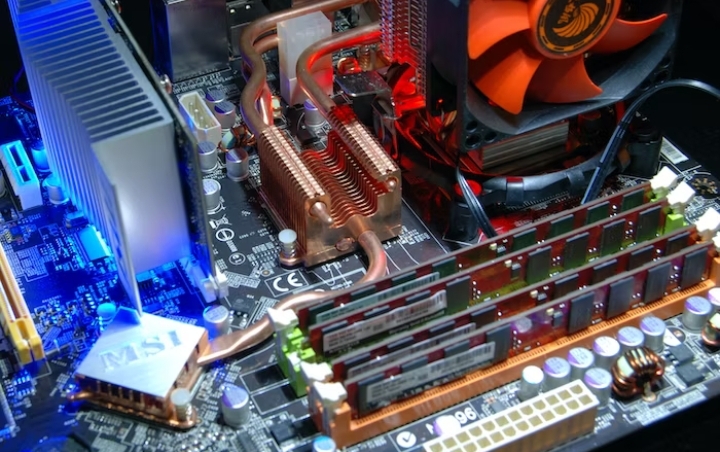
7. Memory
CPU performance can be affected by the type and amount of memory installed in the system. Faster and larger memory modules allow for quicker data access and retrieval, reducing the CPU’s idle time. Moreover, using dual-channel memory configurations can further enhance performance by increasing the memory bandwidth available to the CPU.
8. Software Optimization
Software optimization plays a crucial role in maximizing CPU performance. Well-optimized software takes advantage of the CPU’s capabilities and utilizes its resources efficiently. This includes tasks such as efficient code execution, parallel processing, and minimizing unnecessary computations. When software is optimized for a specific CPU architecture, it can unlock its full potential and deliver enhanced performance.
9. Cooling Solutions
Effective cooling solutions are essential for maintaining optimal CPU performance. When a CPU operates at high temperatures, it can experience thermal throttling, leading to reduced performance. Proper cooling, such as using high-quality heat sinks, fans, or liquid cooling systems, helps dissipate heat efficiently and keeps the CPU at lower temperatures. This ensures consistent performance and minimizes the risk of overheating-related issues.
Conclusion
CPU performance is influenced by various factors that interact with each other to determine the overall speed and efficiency of a computer system. Clock speed, cache size, number of cores, instruction set architecture, TDP, overclocking, memory, software optimization, and cooling solutions all play vital roles in shaping CPU performance. Understanding these factors can help users make informed decisions when selecting a CPU for their specific needs and optimize their system for optimal performance.
FAQs
Q1: Can I increase the clock speed of my CPU to improve performance?
A: Yes, you can overclock your CPU to increase its clock speed and potentially improve performance. However, it should be done cautiously and with proper cooling to avoid overheating and potential damage.
Q2: Does a higher number of cores always result in better performance?
A: Not necessarily. While more cores can improve multitasking and performance in tasks that can utilize multiple cores effectively, single-threaded applications may not benefit significantly from a higher core count.
Q3: How does software optimization impact CPU performance?
A: Software optimization ensures that software utilizes the CPU’s capabilities efficiently, leading to enhanced performance. Well-optimized software can take advantage of parallel processing, minimize unnecessary computations, and execute code efficiently.
Q4: What is the importance of cooling solutions for CPU performance?
A: Cooling solutions are crucial for maintaining optimal CPU performance by dissipating heat effectively. Without proper cooling, CPUs can experience thermal throttling, leading to decreased performance and potential damage.
Q5: Can the amount and type of memory affect CPU performance?
A: Yes, the amount and type of memory can impact CPU performance. Faster and larger memory modules allow for quicker data access and retrieval, reducing CPU idle time and improving overall performance.
Q6: How does the instruction set architecture (ISA) affect CPU performance?
A: Different ISAs have varying capabilities and efficiencies. Choosing the right ISA for a specific task can significantly impact CPU performance and energy efficiency. Common ISAs include x86 and ARM.
Q7: What is thermal throttling?
A: Thermal throttling is a mechanism employed by CPUs to prevent damage due to overheating. When a CPU reaches a certain temperature threshold, it reduces its clock speed to lower heat generation, which can result in decreased performance.
Q8: Can software optimization improve CPU performance on older systems?
A: Yes, software optimization can help improve CPU performance on older systems. Optimized software can utilize available resources more efficiently, potentially enhancing overall performance even on less powerful CPUs.
Q9: How does cache size impact CPU performance?
A: A larger cache size allows the CPU to store frequently accessed instructions and data, reducing the time it takes to fetch information from the main memory. This can result in improved performance, especially in tasks that rely heavily on cache utilization.
Q10: Is CPU performance the only factor that determines overall system performance?
A: No, CPU performance is important but not the sole factor determining overall system performance. Other components such as GPU, memory, storage, and software also contribute to the overall performance of a system. These components work together, and their collective performance impacts the user experience and the system’s ability to handle different tasks efficiently. Therefore, it is crucial to consider the entire system’s configuration and not solely focus on CPU performance when aiming for optimal system performance.