What Is Network Time Protocol? Why Is It Important?
Introduction
In today’s interconnected world, accurate timekeeping is crucial for various computer systems and network devices to synchronize their clocks and perform tasks efficiently. Network Time Protocol (NTP) is a widely used protocol that enables time synchronization across devices connected to a network. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of NTP, its importance, and its role in maintaining accurate timekeeping.
Definition of Network Time Protocol
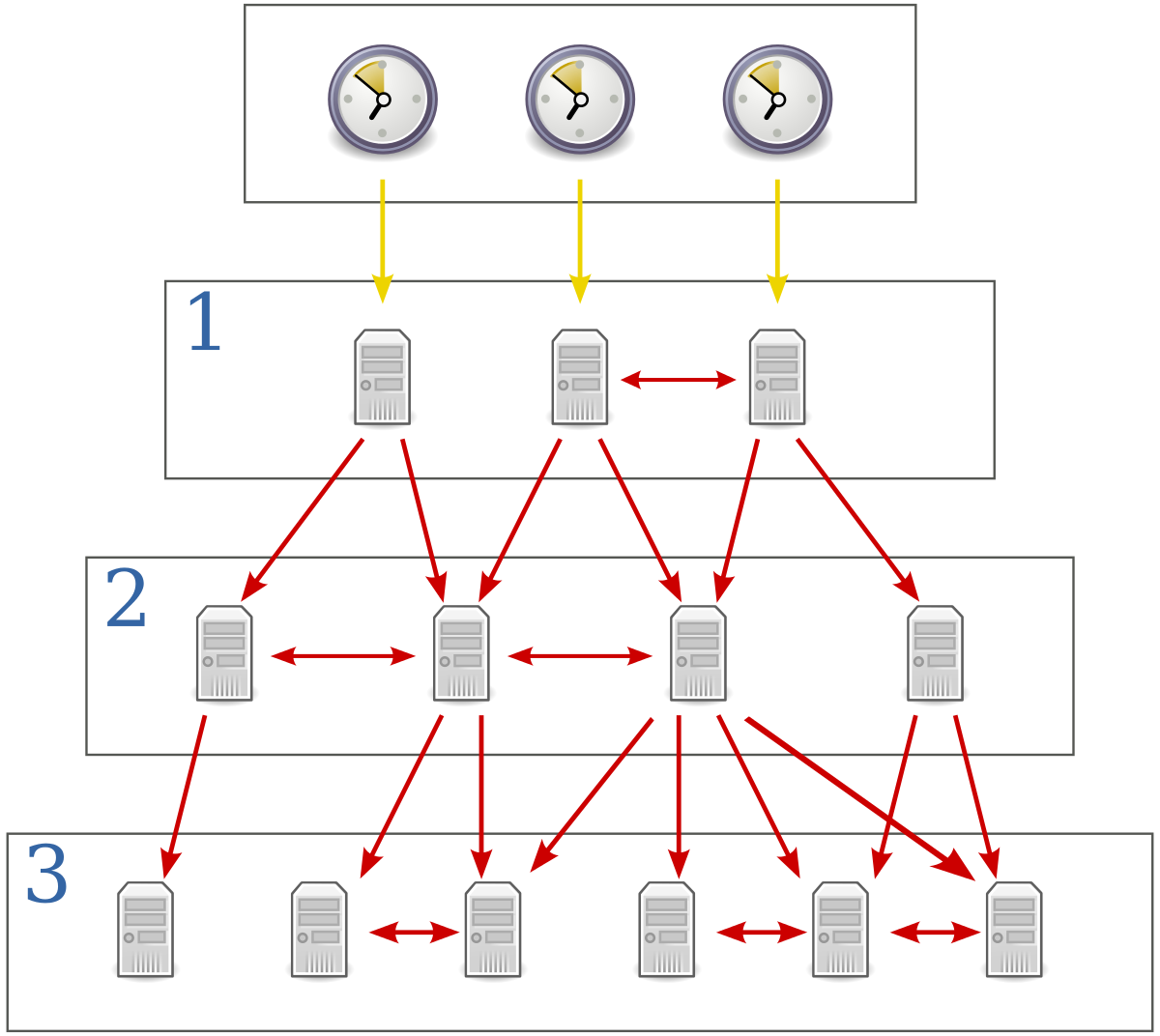
NTP is a networking protocol designed to synchronize the clocks of devices in a network. It utilizes a hierarchical model of time sources, where higher-level time servers provide time references to lower-level servers and devices. NTP uses Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) as the standard time reference, which ensures global synchronization.
How Network Time Protocol Works
NTP operates using a client-server architecture, where the client devices request time updates from NTP servers. The server hierarchy ensures that accurate time information is propagated throughout the network. The time servers themselves synchronize with highly accurate time sources, such as atomic clocks or GPS signals, to provide precise time references to the client devices.
Importance of Network Time Protocol
Accurate timekeeping is essential in various computer systems and network applications. NTP plays a vital role in the following areas:
Network Security: NTP is crucial for ensuring secure communications by synchronizing time-based security mechanisms, such as digital certificates and authentication protocols. Without accurate time synchronization, security measures may fail, leading to potential vulnerabilities.
Log Management: Precise timestamps in log files are essential for troubleshooting, forensic analysis, and compliance audits. NTP ensures that logs from different devices and systems are correctly aligned, enabling effective analysis and identification of issues.
Distributed Systems: In distributed computing environments, where tasks are divided among multiple devices, accurate time synchronization is necessary for coordinated execution and data consistency. NTP ensures that all devices in the distributed system share a common understanding of time.
Financial Transactions: Financial institutions heavily rely on accurate timestamps for transaction records, stock trading, and market analysis. NTP ensures precise timekeeping, preventing discrepancies and ensuring the integrity of financial data.
Benefits of Network Time Protocol
Implementing NTP brings several benefits, including:
Improved Network Performance: By synchronizing clocks, NTP reduces the chance of timing-related errors, enhancing the overall performance and efficiency of networked systems.
Enhanced Security: Accurate time synchronization enables effective security measures, preventing security breaches and unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Compliance and Audit Requirements: NTP assists organizations in meeting regulatory compliance and audit requirements by providing accurate time stamps for events and transactions.
Efficient Troubleshooting: With synchronized logs and timestamps, troubleshooting network issues becomes more streamlined, reducing the time and effort required for problem resolution.
Applications of Network Time Protocol
NTP finds applications in various domains, including:
Network Infrastructure: NTP is widely used in routers, switches, and other network devices to ensure synchronized operations and accurate event logging.
Telecommunications: NTP plays a critical role in telecommunications networks, where precise timekeeping is vital for call routing, billing systems, and synchronization of network elements.
Data Centers: NTP is essential in data center environments to coordinate tasks such as data replication, backup scheduling, and virtual machine migration. It ensures that operations within the data center are synchronized and consistent.
Industrial Control Systems: Industries that rely on precise timing, such as power grids, transportation systems, and manufacturing plants, use NTP to ensure coordination among distributed control systems and devices.
Internet of Things (IoT): With the proliferation of IoT devices, NTP is crucial for maintaining accurate timestamps and synchronization among connected devices, enabling efficient data collection and analysis.
Challenges in Network Time Protocol
While NTP is a robust protocol, it does face certain challenges:
Network Latency: Network delays can impact the accuracy of time synchronization, particularly in geographically dispersed networks. Measures like using regional time servers can help mitigate this challenge.
Network Security: NTP itself does not provide built-in security mechanisms. It is important to secure NTP communications and ensure the integrity of time information by implementing security measures such as encryption and authentication.
Hardware Limitations: Some devices may have limitations in their internal clocks, affecting the precision of timekeeping. Using external time references or upgrading hardware can address this issue.
Best Practices for Implementing Network Time Protocol
To ensure effective implementation of NTP, consider the following best practices:
Use Reliable Time Sources: Choose time servers that synchronize with accurate and reliable time sources, such as atomic clocks or GPS signals, to maintain precise time references.
Implement Redundancy: Employ multiple time servers and distribute them across different network segments to ensure redundancy and resilience in case of server failures or network disruptions.
Secure NTP Communications: Encrypt NTP traffic using protocols like Secure NTP (SNTP) or Transport Layer Security (TLS) to protect time synchronization messages from tampering or eavesdropping.
Monitor and Audit: Regularly monitor the synchronization status of devices and log time-related events. Conduct periodic audits to verify the accuracy and reliability of the timekeeping system.
Conclusion
Network Time Protocol (NTP) is a fundamental protocol for achieving accurate time synchronization in computer networks. Its importance spans across various domains, including network security, log management, distributed systems, and financial transactions. By implementing NTP, organizations can enhance network performance, improve security, meet compliance requirements, and streamline troubleshooting processes.
FAQs
Q: Is NTP the only protocol for time synchronization?
A: No, there are other protocols like Precision Time Protocol (PTP) and Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP), but NTP is the most widely used.
Q: Can NTP be used in both wired and wireless networks?
A: Yes, NTP can be used in both wired and wireless networks to synchronize time among devices.
Q: Is it necessary to have an internet connection for NTP synchronization?
A: While an internet connection can provide access to accurate time references, it is not always necessary. NTP can work with local time servers and reference clocks.
Q: Can NTP handle daylight saving time changes automatically?
A: Yes, NTP is designed to handle daylight saving time changes and adjust the time accordingly.
Q: Is NTP suitable for small-scale networks?
A: Yes, NTP can be implemented in networks of all sizes, from small-scale local networks to large enterprise networks.
Q: Can NTP synchronize time accurately across different time zones?
A: Yes, NTP can synchronize time across different time zones by referencing Coordinated Universal Time (UTC).
Q: Is NTP compatible with IPv6?
A: Yes, NTP fully supports IPv6 and can seamlessly operate in IPv6 networks.
Q: What is the typical accuracy of time synchronization achieved by NTP?
A: With proper configuration and reliable time sources, NTP can achieve time synchronization accuracy within a few milliseconds or even microseconds, depending on network conditions.
Q: Are there any open-source NTP implementations available?
A: Yes, there are several open-source NTP implementations, such as NTPd, Chrony, and OpenNTPD, which provide flexibility and customization options.
Q: Can NTP be used in virtualized environments?
A: Yes, NTP can be used in virtualized environments to synchronize time among virtual machines and host systems. Special considerations may be required to ensure accurate timekeeping in virtualized setups.
Q: Can NTP be used in environments with limited internet access?
A: Yes, NTP can be used in environments with limited internet access by setting up local time servers that synchronize with reliable time references, such as GPS or radio signals.
Q: Is NTP compatible with different operating systems?
A: Yes, NTP is supported by various operating systems, including Windows, Linux, macOS, and Unix-like systems, making it versatile and widely compatible.
Q: How often should NTP synchronization be performed?
A: The frequency of NTP synchronization depends on the specific requirements of the network. In general, regular synchronization at intervals of minutes to hours is recommended for most applications.
Q: Can NTP help in forensic investigations?
A: Yes, accurate timestamps provided by NTP can be valuable in forensic investigations by establishing the sequence of events and aiding in the analysis of system activities.
Q: Does NTP introduce significant network overhead?
A: NTP itself has minimal network overhead. However, it’s important to consider the bandwidth requirements when deploying multiple time servers or when synchronizing a large number of devices.
In conclusion, Network Time Protocol (NTP) plays a crucial role in ensuring accurate time synchronization in computer networks. It enables secure communications, facilitates effective log management, supports distributed systems, and enhances the integrity of financial transactions. By following best practices and considering the specific requirements of the network, organizations can leverage NTP to achieve optimal timekeeping and synchronization, resulting in improved network performance and enhanced security.