The Different Types of Computer Memory & Storage Explained

Introduction
In today’s digital age, computers have become an integral part of our lives. Whether it’s for work or entertainment, we rely on computers to perform various tasks. To understand how computers function, it’s important to grasp the concept of computer memory and storage. In this article, we will explore the different types of computer memory and storage, shedding light on their significance and functionality.
What is Computer Memory?
Computer memory refers to the internal storage space where data and instructions are stored for immediate access by the computer’s processor. It plays a crucial role in the execution of programs and the overall performance of a computer system. There are several types of computer memory, each serving a specific purpose.
Types of Computer Memory
3.1. Random Access Memory (RAM)
Random Access Memory, commonly known as RAM, is a type of computer memory that enables the computer to read and write data quickly. It is considered the working memory of a computer, as it stores data that the processor needs to access frequently. RAM is volatile, meaning its contents are lost when the computer is powered off. It is crucial for multitasking and running applications smoothly.
3.2. Read-Only Memory (ROM)
Read-Only Memory, or ROM, is a type of computer memory that stores data permanently. Unlike RAM, the contents of ROM are not lost when the computer is powered off. It contains firmware or software instructions that are essential for the computer to start up and perform basic functions. ROM is non-volatile and provides a stable foundation for the computer’s operation.
3.3. Cache Memory
Cache memory is a small and ultra-fast type of computer memory that lies between the CPU and main memory. It stores frequently accessed data and instructions to reduce the time taken for the processor to retrieve information from the slower main memory. Cache memory plays a vital role in improving the overall performance of a computer system.
3.4. Flash Memory
Flash memory is a non-volatile type of computer memory that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed. It is commonly used in portable devices like USB flash drives, solid-state drives (SSDs), and memory cards. Flash memory is known for its durability, high-speed data access, and low power consumption.
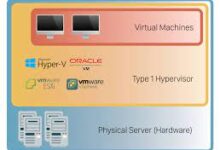
3.5. Virtual Memory
Virtual memory is a technique used by operating systems to extend the available memory beyond the physical limits of the computer. It utilizes a portion of the computer’s hard drive as an extension of RAM, allowing the system to run larger programs and handle more data than the physical memory can accommodate.
What is Computer Storage?
Computer storage refers to the long-term storage of data and programs. It provides a means to store information even when the computer is powered off. Unlike computer memory, storage is non-volatile and can retain data for extended periods.
Types of Computer Storage
5.1. Hard Disk Drive (HDD)
Hard Disk Drives, commonly known as HDDs, are one of the most common types of computer storage. They use magnetic storage to store and retrieve data. HDDs consist of one or more spinning disks or platters coated with a magnetic material. The data is read and written using a magnetic head that moves across the spinning platters. HDDs offer large storage capacities at relatively lower costs, making them ideal for storing large files and applications.
5.2. Solid State Drive (SSD)
Solid State Drives, or SSDs, have gained popularity in recent years due to their faster performance and increased reliability compared to HDDs. SSDs use flash memory technology to store data. Unlike HDDs, SSDs have no moving parts, which results in faster data access times and improved durability. SSDs are more expensive than HDDs but offer significant performance benefits, making them a preferred choice for operating systems and applications that require high-speed storage.
5.3. Optical Drives
Optical drives, such as CD-ROM, DVD-ROM, and Blu-ray drives, use laser technology to read and write data on optical discs. These discs have a reflective surface with microscopic pits and lands that represent binary data. Optical drives are commonly used for reading and writing CDs, DVDs, and Blu-ray discs, making them suitable for storing and accessing multimedia content, software installations, and data backups.
5.4. Magnetic Tape Drives
Magnetic tape drives are a type of computer storage that utilizes magnetic tape to store data. Although not as commonly used in personal computers, magnetic tape drives are often employed for large-scale data backups, archival storage, and data retrieval in enterprise environments. Magnetic tape drives offer high storage capacity and cost-effective long-term data retention.
Comparison between Computer Memory and Storage
While computer memory and storage both play crucial roles in a computer system, they serve different purposes. Computer memory, such as RAM and cache memory, provides temporary storage for data and instructions that the processor needs to access quickly. It enables efficient multitasking and program execution. On the other hand, computer storage, like HDDs, SSDs, optical drives, and magnetic tape drives, offers long-term storage for data, applications, and files even when the computer is powered off.
Computer memory focuses on speed and immediate data access, while storage prioritizes capacity and long-term data retention. Memory is volatile, meaning its contents are lost when power is removed, whereas storage is non-volatile and retains data even without power. Both memory and storage are essential components of a computer system, working together to ensure smooth operation and efficient data management.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of computer memory and storage is crucial for comprehending how computers function and how data is managed. From the volatile and fast-access RAM to the non-volatile and long-term storage provided by HDDs, SSDs, optical drives, and magnetic tape drives, each type of memory and storage serves a specific purpose in the world of computing. By grasping these concepts, users can make informed decisions when it comes to selecting the right memory and storage solutions for their computing needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the primary purpose of computer memory?
Computer memory’s primary purpose is to provide temporary storage for data and instructions that the processor needs to access quickly, enhancing the overall performance of a computer system.
How does RAM differ from storage devices like HDDs and SSDs?
RAM is volatile and provides fast data access for temporary storage, whereas HDDs and SSDs offer non-volatile long-term storage. RAM is essential for multitasking and running programs, while storage devices store data even when the computer is powered off.
Why are SSDs considered faster than HDDs?
SSDs are considered faster than HDDs because they use flash memory technology, which allows for faster data access times. Unlike HDDs, which rely on mechanical spinning disks and moving parts, SSDs have no moving parts and can access data almost instantly. This results in quicker boot times, faster application launches, and improved overall system responsiveness.
What is the advantage of using optical drives?
Optical drives provide the advantage of being able to read and write data on optical discs, such as CDs, DVDs, and Blu-ray discs. This makes them suitable for tasks like installing software, playing multimedia content, and creating data backups. Optical drives also offer a relatively large storage capacity for these types of media.
Are there any drawbacks to using magnetic tape drives?
While magnetic tape drives have their advantages, they also come with some drawbacks. One of the main drawbacks is the relatively slower data access speeds compared to other storage technologies like HDDs or SSDs. Retrieving data from magnetic tapes can take longer, making them less suitable for applications that require quick data access.
Another drawback is the sequential nature of accessing data on magnetic tapes. Unlike random access storage devices like HDDs or SSDs, where data can be accessed directly, magnetic tapes require sequential access. This means that accessing a specific piece of data may require going through a large amount of tape, resulting in longer access times for specific files or data points.
Additionally, magnetic tape drives may require specialized equipment and software for proper operation. They are commonly used in enterprise environments for data backup and archival purposes, but they are not as commonly used in personal computers due to their slower speeds and specific requirements.
Lastly, magnetic tape drives may have limitations in terms of storage capacity compared to other storage technologies. While they can offer high capacities, they may not match the storage capacities available in HDDs or SSDs. This can be a consideration when dealing with large amounts of data that need to be stored and accessed frequently.
Overall, while magnetic tape drives have their niche uses in certain industries, their slower access speeds, sequential data access, and specific requirements make them less suitable for general-purpose storage in personal computers or applications that require fast and random access to data.
What is the future of computer memory and storage?
The future of computer memory and storage is constantly evolving and advancing. One notable trend is the increasing use of solid-state storage, such as SSDs, in various computing devices. SSD technology continues to improve in terms of performance, capacity, and affordability, making it a popular choice for both consumer and enterprise applications.
Another significant development is the emergence of new memory technologies, such as non-volatile memory express (NVMe) and 3D XPoint, which offer even faster data access and higher storage densities than traditional flash memory.
Furthermore, research is being conducted on alternative memory technologies like resistive random-access memory (RRAM), phase-change memory (PCM), and magnetic random-access memory (MRAM), which aim to provide higher speeds, lower power consumption, and increased durability.
In terms of storage, cloud-based storage solutions are becoming increasingly popular due to their scalability, accessibility, and convenience. With the rise of cloud computing, individuals and businesses can store and access their data remotely, eliminating the need for physical storage devices.
Overall, the future of computer memory and storage is focused on faster speeds, higher capacities, lower power consumption, and increased reliability. These advancements will continue to shape the way we store and access data, enabling more efficient and powerful computing experiences.
Can I upgrade the memory and storage of my computer?
Yes, in most cases, you can upgrade both the memory and storage of your computer. Upgrading the memory typically involves adding more RAM modules to increase the amount of available memory. This can improve the performance of your computer, especially when running memory-intensive tasks or multitasking.
Upgrading the storage usually involves replacing the existing storage drive with a larger capacity drive or a faster storage technology like an SSD. This allows you to store more files and data, and it can significantly improve the overall speed and responsiveness of your system.
However, the upgradability of your computer depends on its hardware and design. Some computers, particularly laptops or all-in-one PCs, may have limited upgrade options due to their compact form factor or soldered components. It’s important to check the specifications and documentation of your computer to determine if it supports memory and storage upgrades.
If your computer is upgradable, you can purchase compatible memory modules or storage drives and follow the manufacturer’s instructions or consult a professional technician to install them properly. It’s recommended to research and ensure compatibility before making any upgrades to avoid compatibility issues or potential damage to your computer.
What is the recommended amount of RAM for a computer?
The recommended amount of RAM for a computer depends on the intended use and the operating system requirements. For most general-purpose tasks like web browsing, document editing, and multimedia consumption, 8GB to 16GB of RAM is usually sufficient.
However, if you’re engaging in memory-intensive activities like video editing, graphic design, or gaming, it’s recommended to have 16GB or more of RAM to ensure smooth performance and efficient multitasking.
Keep in mind that different operating systems and software applications have their own recommended or minimum RAM requirements. It’s a good idea to check the specifications of the software you’ll be using and consider future software updates or upgrades when determining the amount of RAM you need for your computer.
Which is better, HDD or SSD?
The choice between HDD and SSD depends on your specific needs and budget. HDDs are more affordable and offer larger storage capacities, making them suitable for situations where cost-effective storage of large amounts of data is required. They are commonly used for mass storage, such as storing media files, documents, and backups.
SSDs, on the other hand, are significantly faster than HDDs and provide faster boot times, quicker application launches, and improved overall system responsiveness. They are more durable, generate less noise, and consume less power. SSDs are recommended for applications where speed and performance are crucial, such as running operating systems, frequently used software, and games.
Many users opt for a combination of both HDD and SSD in their systems, using the SSD as the primary drive for the operating system and frequently accessed programs, while utilizing an HDD for additional storage capacity.
What is the role of cache memory in a computer?
Cache memory plays a vital role in improving the overall performance of a computer system. It is a small and ultra-fast type of memory that sits between the CPU and the main memory. The purpose of cache memory is to store frequently accessed data and instructions, reducing the time it takes for the processor to retrieve information from the slower main memory.
By keeping frequently used data and instructions close to the CPU, cache memory helps minimize the latency and delays associated with accessing data from the main memory. This results in faster data access, improved program execution, and enhanced overall system responsiveness.
Cache memory operates at a higher speed than the main memory but has a smaller capacity. It utilizes different levels, such as L1, L2, and L3 caches, with each level providing varying speeds and capacities. The CPU automatically checks the cache memory first for the required data before accessing the main memory, optimizing performance by reducing the need for frequent and slower main memory access.
Can virtual memory replace physical memory?
Virtual memory is a technique used by operating systems to extend the available memory beyond the physical limits of the computer. It utilizes a portion of the computer’s hard drive as an extension of the physical memory (RAM). While virtual memory can increase the effective memory capacity of a system, it cannot fully replace the need for physical memory.
Physical memory, such as RAM, provides faster data access times compared to virtual memory. Accessing data from virtual memory stored on the hard drive is slower due to the mechanical nature of hard drives. Therefore, physical memory is essential for efficient and fast data access, especially for applications that require frequent and immediate data access, such as running multiple programs simultaneously or working with large datasets.
Virtual memory serves as a supplement to physical memory by temporarily storing less frequently used data and swapping it between the RAM and the hard drive when necessary. It helps prevent system crashes or slowdowns when the physical memory reaches its limit.
However, relying too heavily on virtual memory can result in reduced performance due to the slower data access times of the hard drive. It’s always recommended to have an adequate amount of physical memory to meet the requirements of your operating system and software applications.
What is the difference between volatile and non-volatile memory?
The main difference between volatile and non-volatile memory lies in their ability to retain data when power is removed.
Volatile memory, such as RAM (Random Access Memory), is a type of memory that requires a constant power supply to maintain data integrity. When power is lost or the computer is shut down, the data stored in volatile memory is lost. Volatile memory is essential for temporary storage and data processing, as it allows for fast data access and retrieval.
Non-volatile memory, on the other hand, is a type of memory that retains data even when power is removed. Examples of non-volatile memory include ROM (Read-Only Memory), flash memory, and storage devices like HDDs, SSDs, and optical drives. Non-volatile memory is used for long-term storage of data, applications, and files, ensuring that the information remains intact even when the computer is powered off.
The distinction between volatile and non-volatile memory is crucial for understanding the different roles they play in a computer system. Volatile memory provides temporary storage for data that needs to be accessed quickly, while non-volatile memory offers long-term storage for persistent data that needs to be retained even when the power is turned off.
How does computer memory affect gaming performance?
Computer memory plays a significant role in gaming performance. Sufficient memory capacity and speed can enhance the overall gaming experience by allowing smoother gameplay, reducing lag, and enabling faster loading times.
When playing games, the system needs to store and retrieve game data, textures, models, and instructions quickly. Insufficient memory can lead to frequent loading pauses, choppy frame rates, and overall sluggishness in gameplay.
Having an adequate amount of RAM is crucial for gaming. Modern games often require a significant amount of memory to store and process large amounts of data. With higher memory capacities, the system can keep more game-related data readily available, leading to smoother gameplay and reduced loading times.
Additionally, the speed of the memory, measured in megahertz (MHz), also impacts gaming performance. Faster memory modules allow for quicker data access and transfer, resulting in improved responsiveness and reduced latency during gameplay.
It’s important to check the recommended system requirements for the games you want to play and ensure that your computer meets or exceeds the recommended memory specifications. Upgrading your RAM to meet these requirements can significantly enhance your gaming performance.
How can I optimize my computer’s memory usage?
There are several ways to optimize your computer’s memory usage to ensure efficient performance:
a. Close unnecessary programs: Running too many programs simultaneously can consume a significant amount of memory. Close any programs or background processes that you’re not actively using to free up memory resources.
b. Manage startup programs: Some programs automatically launch at startup, consuming memory even if you’re not using them immediately. Disable or remove unnecessary startup programs to reduce memory usage.
c. Clear temporary files and cache: Temporary files and cache from web browsers and applications can accumulate over time, occupying valuable memory space. Regularly clear these files to free up memory.
d. Increase virtual memory: Adjusting the virtual memory settings can help compensate for limited physical memory. Increase the allocated virtual memory size to provide additional space for data storage when physical memory is running low. This can be done through the system settings or preferences.
e. Optimize system settings: Adjusting system settings can help optimize memory usage. For example, reducing visual effects and animations can free up memory resources. Additionally, disabling unnecessary background services or processes can help minimize memory consumption.
f. Upgrade your RAM: If your computer consistently struggles with memory-intensive tasks or runs out of memory frequently, consider upgrading your RAM. Adding more memory modules can provide the necessary resources for smoother multitasking and improved overall performance.
g. Use a memory optimization tool: There are various software tools available that can help optimize memory usage. These tools can identify memory-hungry processes and optimize memory allocation to maximize performance.
It’s important to note that optimizing memory usage is a continuous process, and it may require a combination of these methods to achieve the best results. Regular maintenance and monitoring of your system’s memory usage can help ensure optimal performance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, computer memory and storage are essential components that significantly impact the performance and functionality of a computer system. Understanding the different types of memory and storage technologies, their advantages, drawbacks, and the factors that influence their performance can help you make informed decisions when it comes to choosing and upgrading your computer’s memory and storage.
From the speed and reliability of solid-state drives (SSDs) to the affordability and high capacity of hard disk drives (HDDs), each technology has its own strengths and best use cases. Additionally, considering factors such as memory capacity, cache memory, and virtual memory can further optimize your computer’s performance and responsiveness.
As technology continues to advance, we can expect further developments in memory and storage, with faster speeds, higher capacities, and more efficient solutions. It’s important to stay updated on the latest trends and advancements to make the most out of your computer system.
By understanding and optimizing your computer’s memory and storage, you can enhance its performance, improve multitasking capabilities, and ensure a smoother user experience.
FAQs
Can I mix different types of memory modules in my computer?
It’s generally recommended to use memory modules of the same type, speed, and capacity to ensure compatibility and optimal performance. Mixing different types or speeds of memory modules may lead to compatibility issues or limited performance.
How often should I upgrade my computer’s memory?
The frequency of memory upgrades depends on your specific needs and the evolving demands of software applications. However, upgrading memory every 2 to 3 years can help keep your computer up-to-date and capable of running the latest software efficiently.
Can I use an external hard drive as additional storage?
Yes, external hard drives can be used as additional storage for your computer. They connect to your computer via USB or other interfaces and provide additional space for storing files, documents, and multimedia content.
Is it possible to upgrade the memory of a laptop?
In many cases, the memory of a laptop can be upgraded. However, the upgradability depends on the laptop’s specific model and design. It’s recommended to check the laptop’s documentation or consult a professional technician to determine if memory upgrades are possible.
Do all computers have cache memory?
Yes, almost all modern computers have cache memory. It is an integral part of the CPU architecture and is used to improve data access speeds and overall system performance. The size and levels of cache memory can vary depending on the CPU model and design.
What is the difference between RAM and ROM?
RAM (Random Access Memory) is a volatile memory that stores data and instructions temporarily during the computer’s operation. ROM (Read-Only Memory), on the other hand, is a type of non-volatile memory that contains pre-programmed data and instructions. While RAM can read from and write to data, allowing for dynamic changes, ROM retains its contents even when the power is turned off and cannot be modified by normal computer operations.
Can I upgrade the storage capacity of my smartphone?
The storage capacity of smartphones can be upgraded in some cases. However, it depends on the specific model and design of the smartphone. Some smartphones have expandable storage options, such as microSD card slots, which allow you to insert a memory card to increase storage capacity. On the other hand, many smartphones come with fixed internal storage that cannot be upgraded.
Is it necessary to defragment an SSD?
No, it is not necessary to defragment an SSD. Unlike traditional hard disk drives (HDDs), SSDs use flash memory technology, which does not suffer from the same fragmentation issues as HDDs. In fact, defragmenting an SSD can actually reduce its lifespan and have minimal to no performance benefits. It’s best to avoid defragmenting SSDs and focus on regular maintenance tasks like clearing unnecessary files and optimizing system settings.
What is the difference between RAM and VRAM?
RAM (Random Access Memory) and VRAM (Video RAM) serve different purposes in a computer system. RAM is general-purpose memory that is used by the CPU to store and access data and instructions for running applications. It is shared among various processes and tasks.
VRAM, on the other hand, is a specific type of memory dedicated to graphics processing. It is used by the GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) to store and manipulate graphical data, such as textures, shaders, and frame buffers. VRAM is optimized for high-speed access and is essential for smooth and efficient graphics rendering in games and other visually demanding applications.
Can insufficient memory cause my computer to freeze or crash?
Yes, insufficient memory can cause your computer to freeze, slow down, or even crash. When the available memory is overwhelmed by the demands of running multiple programs or memory-intensive tasks, the system may become unresponsive, leading to freezing or crashing. Upgrading your computer’s memory can help alleviate these issues and provide a smoother and more stable computing experience.
What are the benefits of using ECC memory?
ECC (Error-Correcting Code) memory is a type of RAM that includes additional circuitry to detect and correct memory errors. It is commonly used in mission-critical systems, such as servers and workstations, where data integrity is of utmost importance.
The primary benefit of ECC memory is its ability to identify and correct single-bit memory errors, ensuring that data stored in memory remains accurate and consistent. This is crucial for applications that involve financial transactions, data processing, scientific research, or any situation where data accuracy is critical. By detecting and correcting errors, ECC memory helps prevent data corruption, system crashes, and potential security vulnerabilities.
Another benefit of ECC memory is its ability to detect and report multiple-bit errors. While it cannot correct these errors, it provides an important notification to the system administrator, allowing for timely investigation and resolution.
ECC memory provides an extra layer of reliability and stability to the system, reducing the risk of data loss or system failures. It is particularly valuable in environments where data integrity is paramount, such as server farms, scientific research facilities, and financial institutions.
However, it’s important to note that ECC memory comes at a higher cost compared to non-ECC memory, and not all systems or applications require its level of error correction. For most consumer-grade systems, non-ECC memory is sufficient and offers a more cost-effective solution.
In conclusion, ECC memory offers enhanced data integrity and error correction capabilities, making it an ideal choice for mission-critical systems that require the utmost reliability and stability. For everyday consumer use, non-ECC memory provides adequate performance and affordability. The choice between ECC and non-ECC memory ultimately depends on the specific needs and requirements of the system or application.
FAQs
Can I mix ECC and non-ECC memory modules in my server?
It is generally recommended to use either ECC or non-ECC memory modules in a server, but not both simultaneously. Mixing ECC and non-ECC memory modules can result in unpredictable behavior and may compromise the system’s overall reliability and error correction capabilities.
Is it possible to upgrade the memory of a smartphone or tablet?
Upgrading the memory of a smartphone or tablet is not always possible, as many mobile devices have non-expandable internal memory. However, some devices may offer models with different storage capacities, allowing you to choose a higher-capacity variant when purchasing.
What is the difference between DDR3 and DDR4 memory?
DDR3 (Double Data Rate 3) and DDR4 (Double Data Rate 4) are different generations of RAM. DDR4 memory offers higher data transfer rates, improved power efficiency, and increased memory capacity compared to DDR3. However, compatibility between DDR3 and DDR4 memory modules is not possible due to differences in the physical design and memory controller support.
Is it necessary to power off the computer when upgrading memory modules?
It is generally recommended to power off the computer before upgrading memory modules to ensure safety and prevent any potential damage. Additionally, turning off the power ensures that the system recognizes the new memory configuration during startup.
Can I install more RAM than the maximum supported by my computer’s motherboard?
No, you cannot install more RAM than the maximum supported by your computer’s motherboard. The maximum supported memory is determined by the motherboard’s design and specifications. Exceeding this limit may result in system instability or failure to recognize the additional memory modules.
Can I use server memory in a desktop computer?
Server memory modules, such as ECC memory, are designed for specific server architectures and may not be compatible with desktop computers. It is recommended to use memory modules specifically designed for desktop systems to ensure compatibility and optimal performance.