What Is Near-Field Communication (NFC)? How Does It Work?
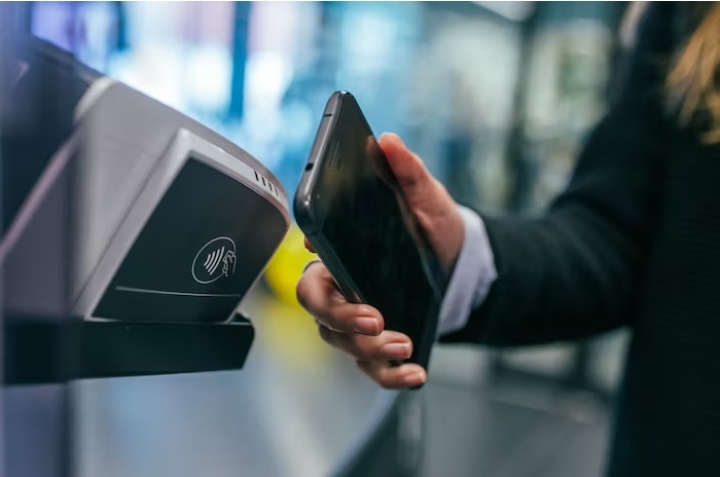

You probably use it most times for contactless payments, but do you know how NFC actually work?
Contactless payments are popular in modern society. NFC, short for near-field communication, is the name of the technology that enables contactless payments. NFC has many applications, but regrettably, fraudsters have the potential to abuse it. What what is near-field communication, how does it work, and what are the dangers involved? Let’s find out!
What is Near-Field Communication (NFC)?
NFC is simply a wireless technology that enables close-range communication between devices. And by short, we mean incredibly short. The highest range of NFC is about 10 cm. Because of this, GPS tracking, streaming, social networking, and other tasks that need for a long-distance connection are not appropriate for near-field communication.
Instead, NFC is made especially for the transmission of communication between two NFC-capable objects. To communicate using this approach, both parties must have the NFC feature turned on and be close by. For instance, both smartphones would need to have the NFC feature turned on if they wanted to communicate using NFC. You may need to manually activate the NFC feature on your device because it doesn’t always come activated.
NFC technology and its applications
NFC technology combines the principles of both contactless card technology and RFID. It allows devices to establish two-way communication by creating a radio frequency field. This technology finds extensive use in various industries and applications, including mobile payments, transportation, healthcare, retail, and more.
Read Also: What Are VPCs and Subnets in Cloud Computing & How Do They Work?
Key Components of NFC
NFC consists of two main components: the NFC reader/writer and the NFC tag. The NFC reader/writer is usually integrated into a device such as a smartphone, tablet, or computer, while the NFC tag is a passive component that contains the data to be exchanged. These components work together to enable seamless communication and data transfer.
How does NFC work?

NFC operates in two communication modes: active and passive. In active mode, both the NFC reader/writer and the NFC tag generate their own radio frequency fields. In passive mode, the NFC reader/writer generates the radio frequency field, and the NFC tag only uses that field to power itself and respond.
The NFC operating frequency of 13.56 MHz allows for reliable and efficient communication. The range of NFC is typically limited to a few centimeters, ensuring close proximity is required for successful data transfer.
NFC data transfer occurs through electromagnetic induction. When an NFC-enabled device is brought near an NFC tag, the electromagnetic field induces a current in the tag’s antenna. This current powers the tag and enables it to transmit data back to the device. The data transfer process involves a series of modulation and demodulation techniques to ensure accurate and secure communication.
NFC supports different modes of data transfer, including peer-to-peer mode and card emulation mode. In peer-to-peer mode, two NFC-enabled devices can exchange data by taking turns acting as both the sender and receiver. This mode is commonly used for tasks like sharing files, contacts, or initiating wireless payments between smartphones.
On the other hand, card emulation mode allows an NFC-enabled device to act as a contactless card or tag. This mode enables compatibility with existing contactless card infrastructure, making it suitable for applications like mobile payments and access control systems.
Read Also: What Is Beamforming? How Does It Make Your Wi-Fi Faster?
NFC-enabled devices
NFC technology is supported by a wide range of devices, including smartphones, tablets, wearables, and IoT devices. Let’s explore some of the common examples:
Smartphones and tablets: Many modern smartphones and tablets come equipped with NFC capabilities. This allows users to enjoy the convenience of mobile payments, share content, and connect with other NFC-enabled devices effortlessly.
NFC tags and cards: NFC tags and cards are small, passive devices that can store information and be read by NFC-enabled devices. They are commonly used in applications like access control, product authentication, and interactive advertising.
Wearables and IoT devices: NFC technology is increasingly being integrated into wearable devices like smartwatches, fitness trackers, and even clothing. This enables seamless connectivity and easy pairing with other devices.
NFC use cases and applications
NFC has found widespread adoption in various industries due to its versatility and convenience. Here are some of the notable use cases and applications of NFC:
Mobile payments and digital wallets: NFC enables contactless payments through mobile wallets like Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Samsung Pay. Users can simply tap their NFC-enabled smartphones or smartwatches on compatible payment terminals to make secure transactions.
Contactless ticketing and access control: NFC is extensively used for contactless ticketing systems in transportation networks, stadiums, and events. It allows users to store their tickets digitally on their smartphones or NFC cards, simplifying the entry process.
Data exchange and sharing: NFC facilitates seamless sharing of files, contacts, and other digital content between NFC-enabled devices. This feature is particularly useful for quick sharing in business meetings, social interactions, and content distribution.
Smart home automation: NFC can be integrated with smart home devices to enable convenient control and automation. By tapping an NFC-enabled device on specific tags or readers, users can activate pre-set actions like turning on/off lights, adjusting temperature, or playing music.
Healthcare and medical applications: NFC technology plays a vital role in healthcare for patient identification, access control, and secure data transfer. It can be used to track medical equipment, provide medication information, and enable efficient healthcare management systems.
Read Also: Chroma Subsampling: What Is It and Why Does It Matter?
Advantages of NFC technology
Simplicity and ease of use: NFC offers a user-friendly experience with its simple tap-and-go functionality. It eliminates the need for complex setup procedures or manual pairing, making it accessible to a wide range of users.
Interoperability: NFC is compatible with existing contactless card infrastructure, allowing smooth integration with various systems and applications. It enables interoperability between different devices and platforms.
Security: NFC employs encryption and authentication protocols to ensure secure data transmission. It provides a layer of protection against unauthorized access and data breaches, making it suitable for sensitive applications like mobile payments.
Limitations and challenges of NFC
Limited range: The short-range nature of NFC, although necessary for security purposes, limits its applicability to certain scenarios. Users need to bring their devices in close proximity for successful communication, which may not be ideal for certain use cases that require longer-distance connectivity.
Dependency on device compatibility: NFC functionality requires both the sending and receiving devices to have NFC capabilities. While many modern smartphones and devices support NFC, it may not be universally available across all devices, limiting its widespread adoption.
Data transfer speed: While NFC provides a convenient way to exchange small amounts of data, its transfer speed is relatively slower compared to other wireless technologies like Bluetooth or Wi-Fi. This makes it less suitable for transferring large files or streaming data-intensive content.
NFC security considerations
Ensuring the security of NFC transactions and data exchange is crucial. NFC incorporates various security measures to protect user information and prevent unauthorized access:
Encryption and authentication: NFC uses encryption algorithms to secure data during transmission. Additionally, authentication protocols verify the identities of devices involved in the communication process, preventing potential tampering or interception.
Secure Element and Host Card Emulation: NFC-enabled devices often include a secure element, which is a tamper-resistant hardware component that stores sensitive information like payment credentials. Host Card Emulation (HCE) is an alternative software-based approach that emulates the functionality of a secure element, providing secure transactions without the need for additional hardware.
Future developments and trends in NFC
The future of NFC technology holds promising advancements and potential applications:
Enhanced functionality: NFC is expected to evolve with new features and capabilities, such as increased data transfer speeds, extended range, and improved compatibility with other wireless technologies. This will open up new possibilities for its utilization in areas like smart cities, IoT connectivity, and advanced payment solutions.
Integration with emerging technologies: NFC is likely to integrate with emerging technologies like augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and machine learning (ML). This convergence will result in innovative applications and seamless user experiences.
Industry-specific applications: NFC will continue to find applications in specific industries like healthcare, transportation, retail, and logistics. For example, NFC-enabled medical devices can enhance patient monitoring and medication management, while NFC-based supply chain solutions can improve inventory tracking and product authentication.
Read Also: What Is a Reverse Proxy and How Does It Work?
Conclusion
Without a doubt, NFC can enable smooth, contactless payments and also makes a variety of tasks much easier. But regardless of whether you regularly use NFC or are thinking about trying it out, it’s important to be aware of the security dangers associated with this technology.
FAQs
What devices support NFC technology?
NFC technology is supported by various devices, including smartphones, tablets, wearables (smartwatches, fitness trackers), and IoT devices. Many modern smartphones come with built-in NFC capabilities.
How secure is NFC for mobile payments?
NFC technology employs encryption and authentication protocols to ensure secure mobile payments. It provides a secure channel for transmitting payment information between devices, offering a high level of security.
Can NFC be used for data transfer between different smartphone platforms?
Yes, NFC allows data transfer between different smartphone platforms. It operates independently of the operating system, making it compatible with devices running Android, iOS, or other platforms.
Can NFC be used without an internet connection?
Yes, NFC can be used without an internet connection. It relies on short-range wireless communication between devices, eliminating the need for internet connectivity during data transfer.
Can NFC be used for contactless access control systems?
Yes, NFC is commonly used for contactless access control systems in various environments such as offices, hotels, and public transportation. NFC-enabled cards or smartphones can be used to authenticate and grant access to restricted areas or services.
What are some popular mobile payment systems that utilize NFC?
Popular mobile payment systems that utilize NFC include Apple Pay, Google Pay (formerly Android Pay), Samsung Pay, and various banking and financial institution-specific payment apps.
Can NFC tags be reprogrammed or reused?
Yes, NFC tags can be reprogrammed and reused multiple times. They can be written with new information or commands, allowing them to be used for different purposes or in different contexts.
Is NFC limited to short-range communication only?
Yes, NFC is designed for short-range communication, typically within a few centimeters. This limited range ensures secure and controlled data transfer between devices.