How Does a Router Work? A Simple Explanation

Routers may seem to be complicated because but they are actually very simple. Here’s an overview on routers, including what they do and how they work.
Routers are a vital piece of technology that most of us have in our homes, yet many of us are unfamiliar with them. In reality, most individuals are unaware of what a router is and how it differs from a modem.
Fortunately, we are here to demystify the basic features of a router so that you can more easily understand your network devices.
So, what role does a router play in a network? How does a router function? Let’s find out.
What is a Router?
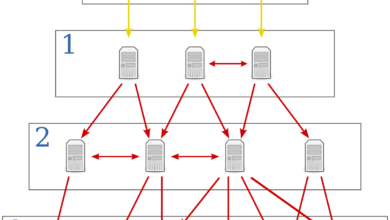
Before we go into how a router works, let’s first understand what a router is. In simple terms, a router is a networking device that directs data packets between computer networks. It acts as a traffic cop, determining the most efficient path for data to travel from its source to its destination. Routers can be found in homes, offices, and even large-scale data centers, enabling communication across local area networks (LANs) and wide area networks (WANs).
How Does a Router Work?
A. Data Packet Routing
At the core of a router’s functionality is its ability to route data packets. When you send a request or perform an action on your device that requires internet access, such as loading a webpage, the data is broken down into small packets. These packets contain not only the information you requested but also the necessary addressing details, such as the source and destination IP addresses.
The router examines these packets and consults its routing table, a database that contains information about the networks it is connected to. Based on the destination IP address, the router determines the best path for the packet to travel and forwards it to the appropriate network. This process continues until the packet reaches its final destination, where it is reassembled to form the complete data.
B. Network Address Translation (NAT)
In addition to routing data packets, routers also perform Network Address Translation (NAT). NAT allows multiple devices in a network to share a single public IP address provided by the internet service provider (ISP). This technology is crucial in conserving IPv4 addresses, as the number of available addresses is limited.
When data packets leave a local network and are destined for the internet, the router replaces the private IP addresses of the devices with its public IP address. This way, the router acts as an intermediary, shielding the individual devices from direct exposure to the internet. When the response packets arrive, the router uses NAT to reverse the process and deliver the data to the correct device within the local network.
C. DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
Another important function of routers is their support for DHCP, or Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. DHCP allows routers to assign IP addresses automatically to devices within a network. Instead of manually configuring IP addresses for each device, DHCP simplifies the process by dynamically assigning unique IP addresses to devices as they connect to the network.
When a device joins a network, it sends a DHCP request to the router, which then allocates an available IP address from a predefined pool. This eliminates the need for manual IP address management and ensures efficient network utilization.
Read Also: What Is the WPS Button on My Router?
D. Firewall Protection
Routers also provide an added layer of security through built-in firewall protection. Firewalls analyze the incoming and outgoing data packets and apply security rules to determine whether they should be allowed or blocked. This helps protect the network from unauthorized access, malicious attacks, and potential vulnerabilities.
Firewalls can be configured to filter specific types of traffic, such as blocking certain ports or protocols. They act as a barrier between the internal network and the external internet, monitoring and controlling the flow of data to ensure a secure environment.
What are the Components of a Router?
To understand how a router functions, it’s essential to familiarize yourself with its key components.
A. CPU (Central Processing Unit)
The CPU of a router is responsible for executing the instructions and performing the necessary computations. It processes data packets, manages routing tables, and handles various protocols. The performance and processing power of the CPU impact the overall speed and efficiency of the router.
B. Memory
Routers have different types of memory, such as RAM (Random Access Memory) and ROM (Read-Only Memory). RAM is used for temporary storage of data packets, routing tables, and other operational information. ROM contains the router’s firmware, which provides the basic instructions for the router’s operation.
C. Interfaces
Interfaces are the physical ports on a router that connect it to other devices or networks. Common types of interfaces include Ethernet ports, Wi-Fi antennas, and WAN ports. These interfaces enable the router to establish connections and facilitate data transfer between different networks or devices.
V. Types of Routers
Routers come in various types, each designed for specific use cases. Here are three common categories:
A. Home Routers
Home routers are typically used in residential settings to connect devices within a household to the internet. They often include built-in Wi-Fi capabilities and offer basic routing functionalities suitable for everyday use.
B. Enterprise Routers
Enterprise routers are designed for larger organizations and businesses. They have more advanced features, such as enhanced security options, higher performance capabilities, and support for multiple WAN connections. Enterprise routers are commonly used in offices, campuses, and data centers.
C. Service Provider Routers
Service provider routers are used by internet service providers (ISPs) to manage and route data across their networks. These routers handle large volumes of traffic, ensure efficient data transmission, and support various protocols and technologies required for internet connectivity on a broader scale.
How to Set Up a Router
Setting up a router involves two primary steps which are; physical connection and configuration settings.
A. Physical Connection
To start, connect your router to a power source and use Ethernet cables to establish connections between the router and your modem. This allows the router to receive internet signals from the modem and distribute them to connected devices.
B. Configuration Settings
Once the physical connections are in place, access the router’s configuration interface through a web browser. Here, you can set up essential parameters, such as network name (SSID), Wi-Fi password, security settings, and other preferences. It’s advisable to follow the manufacturer’s instructions or consult the user manual for specific configuration steps.
Read Also: What Is Beamforming? How Does It Make Your Wi-Fi Faster?
Conclusion
Routers are essential networking devices that play a vital role in connecting devices and facilitating communication over networks. By understanding the basic principles of how routers work, including data packet routing, network address translation, DHCP, and firewall protection, you can gain insight into their functionality.
Moreover, familiarizing yourself with the components of a router and the different types available, such as home routers, enterprise routers, and service provider routers, allows you to choose the right router for your specific needs.
Setting up a router involves physical connections and configuration settings, both of which can be easily accomplished with proper guidance. In case of troubleshooting router issues, following the suggested steps can help resolve common problems and ensure optimal router performance.
Routers serve as the backbone of our interconnected world, enabling seamless communication and access to information. With a clear understanding of how routers work, you can navigate the networking landscape with confidence and make the most of your internet experience.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I use a router without an internet connection?
Yes, routers can be used to create local networks for file sharing, printing, or device-to-device communication, even without an internet connection.
Do all routers have Wi-Fi capabilities?
No, not all routers have built-in Wi-Fi capabilities. Some routers are designed specifically for wired connections, while others include Wi-Fi functionality.
Can I use any router with my internet service?
In most cases, you can use any router with your internet service, but it’s important to ensure compatibility with your ISP’s requirements and the type of connection you have.
What is the range of a typical home router’s Wi-Fi signal?
The Wi-Fi signal range of a home router can vary depending on factors such as the router’s power, antenna design and environmental conditions. Generally, a typical home router can provide coverage within a range of 100-150 feet indoors, but this range can be affected by walls, obstacles, and interference.
Can I connect multiple devices to a router?
Yes, routers are designed to connect multiple devices simultaneously. They typically have multiple Ethernet ports and provide Wi-Fi connectivity for wireless devices, allowing you to connect smartphones, laptops, smart TVs, gaming consoles, and more.
Can I secure my router from unauthorized access?
Absolutely. It’s crucial to secure your router to prevent unauthorized access to your network. You can enable encryption protocols like WPA2/WPA3, change default login credentials, and disable remote management for enhanced security.
What is the difference between a modem and a router?
A modem connects your network to the internet service provided by your ISP, while a router directs data packets between devices within a network. Some devices combine the functions of a modem and a router into a single unit.
Can I use a router to extend Wi-Fi coverage in my home?
Yes, you can use additional routers or devices called Wi-Fi extenders or repeaters to extend the Wi-Fi coverage in your home. These devices help amplify and extend the wireless signal to reach areas with weaker coverage.
Can I connect a router to another router?
Yes, it’s possible to connect routers together to expand network coverage or create separate network segments. This can be achieved by configuring one router as the primary router and the other as a secondary router or access point.
Can I use a router with a mobile broadband connection?
Yes, routers are available that support mobile broadband connections. These routers typically have built-in SIM card slots or USB ports to connect to mobile networks and provide Wi-Fi access to multiple devices.
What are some advanced features to look for in a router?
Advanced features to consider include Quality of Service (QoS) for prioritizing certain types of traffic, parental controls for managing internet access for children, VPN support for secure remote connections, and guest network functionality.
Can I use a router to improve online gaming performance?
Yes, routers with features like Quality of Service (QoS), low latency, and prioritization settings can help improve online gaming performance by optimizing network traffic and reducing lag during gameplay.